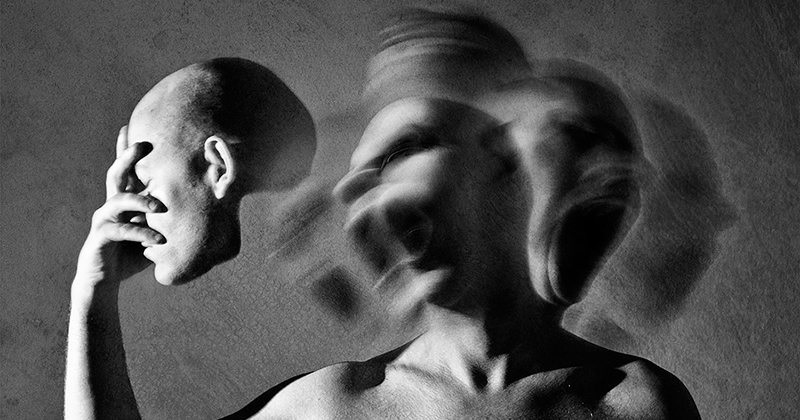
Schizophrenia is a persistent mental disease that impacts:
- emotions
- the capacity to believe reasonably and plainly
- the capability to communicate with and relate to others
According to the National Association on Mental Illness, schizophrenia influences about one percent of Americans. It’s typically detected in late teenage years or early 20s for males, and late 20s or very early 30s in ladies.
Episodes of the ailment can come and go similar to an illness in remission. When there’s an “energetic” period, a person may experience:
- hallucinations
- deceptions
- problem reasoning and focusing
- a flat affect
Subtypes of schizophrenia
Although the subtypes do not exist as separate professional disorders any longer in schizophrenia clinical trials, they can still be useful as indicators and for treatment planning. There are five classical subtypes:
- Paranoid schizophrenia
The subtype description is still used though, because of exactly how usual it is. Signs include:
-
- delusions
- hallucinations
- disorganized speech, for example, word salad, echolalia
- difficulty focusing
- behavioral disability, such as impulse control, emotional lability
- level effect
- Hebephrenic/disorganized schizophrenia
In this variation of schizophrenia, the person doesn’t have hallucinations or delusions. Instead, they experience topsy-turvy habits and speech. This can include:
- flat affect
- speech disturbances
- topsy-turvy reasoning
- improper feelings or face responses
- the trouble with daily activities
- Undifferentiated schizophrenia
Uniform schizophrenia was the term utilized to describe when a specific presented action that applied to more than one type of schizophrenia.
- Recurring schizophrenia
Recurring schizophrenia usually consists of more “unfavorable” signs, such as:
-
- squashed affect
- psychomotor problems
- slowed down speech
- inadequate health
- Catatonic schizophrenia
It normally presents itself as immobility, however, can also resemble:
- imitating behavior
- mutism
- a stupor-like problem
Schizophrenia in Children
Childhood year’s schizophrenia isn’t a subtype; however, instead of utilized to refer to the time of diagnosis. Medical diagnosis in kids is rather unusual.
Signs in kids are similar to those of developing disorders, such as autism, as well as attention-deficit hyperactivity disease. These signs and symptoms can include:
- language delays
- late or unusual crawling or walking
- unusual motor activities
Signs and symptoms in older kids and teens include:
- social withdrawal
- rest disturbances
- damaged college performance
- impatience
- weird actions
- compound use









Comments